In Canada, where timely and effective emergency response can be
BLS Your First Response in a Life-Threatening Emergency
Basic Life Support
BLS is a set of life-saving procedures designed to support someone experiencing a medical emergency. These techniques are crucial for maintaining breathing and circulation until advanced medical care arrives. This page provides a general overview of BLS. However, it is not a substitute for certified training. To learn these skills properly and become certified, please [link to your course page or relevant resources].
What We Do

What is Basic Life Support (BLS)?
BLS involves a series of non-invasive interventions aimed at stabilizing a person in critical conditions. The primary focus of BLS is on the “ABCs”:
Airway
Ensuring the airway is open and clear.
Breathing
Supporting or restoring breathing.
Circulation
Maintaining blood circulation.
Important knowledge about
Basic Life Support

- Disclaimer
- ACTIVATE EMERGENCY RESPONSE
- Essential BLS Steps: A Quick Guide
- When is BLS Needed?
This information provides a general overview of BLS. It is not a substitute for certified training. Proper BLS training includes hands-on practice, feedback from certified instructors, and certification upon successful completion.
PRIORITY #1: ACTIVATE EMERGENCY RESPONSE
- Call First: The very first action in most BLS scenarios is to call for help. In Canada, dial 911.
- If you are alone, call 911 before providing care to an unresponsive adult who is not breathing or only gasping.
- If someone else is present, delegate the task of calling 911.
- Provide the dispatcher with clear information:
- Your location
- The nature of the emergency
- The number of victims
- Do not hang up until the dispatcher tells you to.
Then, if needed, proceed with the following BLS steps:
Scene Safety: Ensure the area is safe for both you and the victim before approaching.
Responsiveness Check:
- Gently tap or shake the person’s shoulder.
- Shout, “Are you okay?”
- Observe for any response (movement, speaking, etc.).
Breathing Check:
- Look for chest rise and fall for no more than 10 seconds.
- If the person is not breathing or only gasping, proceed to CPR.
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation):
- Call 911 (if not already done).
- Chest Compressions:
- Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest.
- Interlock your fingers.
- Compress the chest at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Compress to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) in adults.
- Cycles:
- Continue cycles of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths (if trained).
Rescue Breaths (If Trained):
- If trained, after opening the airway, give 2 rescue breaths.
- Each breath should last about 1 second and make the chest rise.
AED (Automated External Defibrillator):
- If an AED is available, retrieve and use it as soon as possible.
- Follow the device’s voice prompts.
Choking:
- BLS also includes techniques to relieve choking, such as abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver).
Recovery Position:
- If the person regains consciousness and is breathing normally, and you’re sure there are no spinal injuries, carefully place them in the recovery position to help keep the airway open.
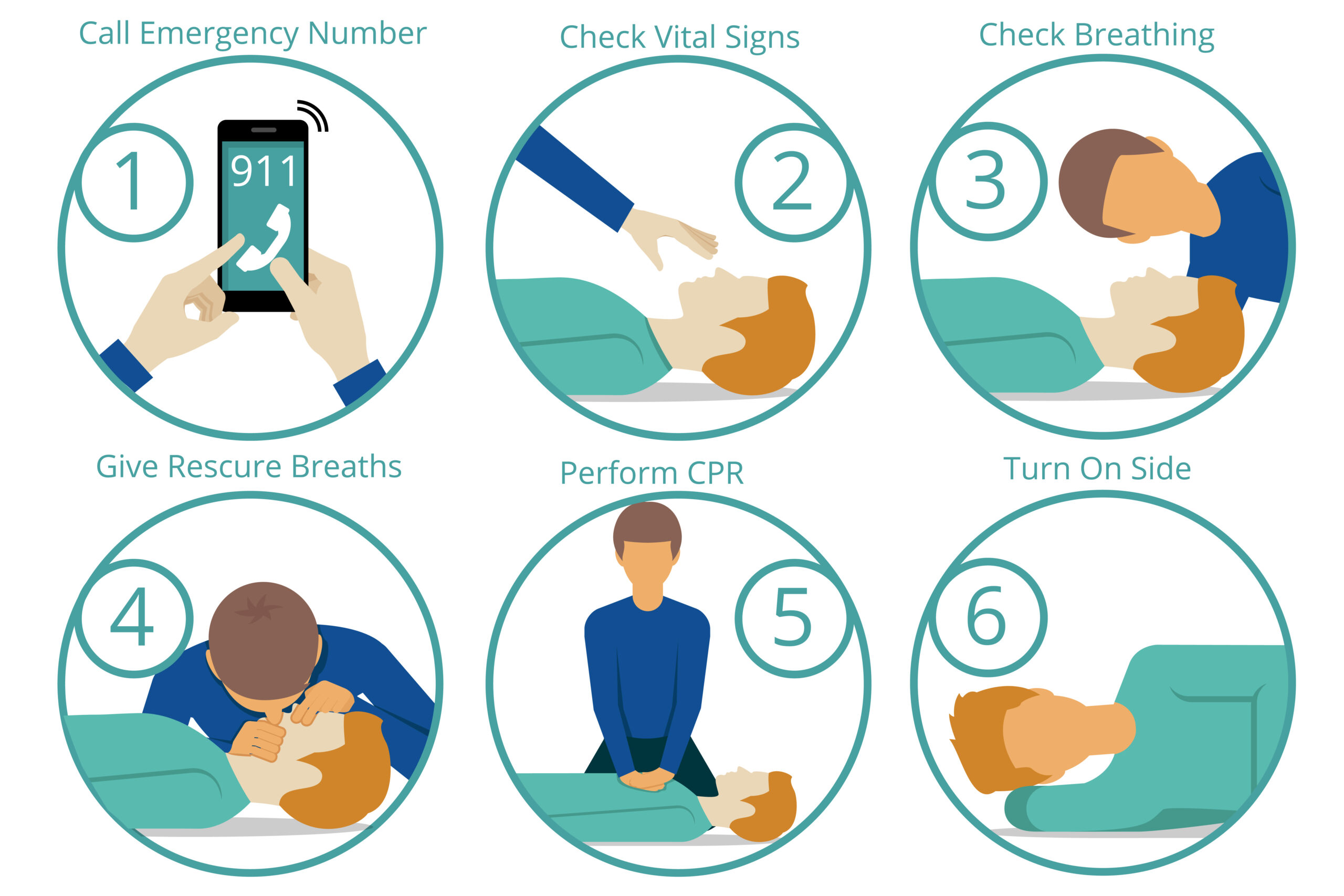
These steps outline the core actions of Basic Life Support (BLS) to assist someone in a life-threatening emergency. Remember, this is a simplified guide. Formal BLS training is crucial for proper technique and certification.
BLS Steps
(1) Call Emergency Number
- Immediately dial the appropriate emergency number (911 in most of Canada) to activate the emergency medical system.
- Provide the dispatcher with the location, the situation, and the number of victims.
- Don’t hang up until instructed.
(2) Check Responsiveness
- Gently tap or shake the person’s shoulder.
- Shout, “Are you okay?”
- Observe for any response (movement, speaking, etc.).
(3) Check Breathing
- Look for chest rise and fall for no more than 10 seconds.
- If the person is not breathing or only gasping, proceed to CPR.
(4) Give Rescue Breaths (If Trained)
- If trained, after opening the airway, give 2 rescue breaths.
- Each breath should last about 1 second and make the chest rise.
(5) Perform CPR
- Chest Compressions:
- Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest.
- Interlock your fingers.
- Compress the chest at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
- Compress to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) in adults.
- Cycles:
- Continue cycles of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths (if trained).
(6) Turn On Side (Recovery Position)
- If the person regains consciousness and is breathing normally, and you’re sure there are no spinal injuries, carefully place them in the recovery position.
- This helps keep the airway open.
Important Reminders:
- AED (Automated External Defibrillator): If an AED is available, use it as soon as possible and follow the device’s prompts.
- Continue: Keep performing BLS until emergency services arrive or the person recovers.
- Training is Key: This guide is for informational purposes only. Enroll in a certified BLS course to learn these skills properly.
BLS is typically used in emergencies such as:
- Cardiac arrest (when the heart stops beating)
- Respiratory arrest (when breathing stops)
- Choking
- Unresponsiveness
Cardiac arrest
(when the heart stops beating)
This life-threatening condition occurs when the heart’s electrical system malfunctions, causing it to stop pumping blood effectively, leading to a loss of consciousness and cessation of normal breathing. Immediate intervention with CPR and defibrillation is crucial to increase the chance of survival.
Respiratory arrest
(when breathing stops)
Respiratory arrest happens when breathing ceases or becomes ineffective, preventing the lungs from adequately oxygenating the blood, which can be caused by various factors such as airway obstruction, drug overdose, or neurological conditions. Prompt recognition and rescue breathing are essential to provide oxygen to the body until the person can breathe on their own or advanced care is available.
Choking
Choking occurs when a foreign object obstructs the airway, blocking the flow of air to the lungs and potentially leading to respiratory distress or arrest if not quickly resolved. Effective techniques like abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) are vital to dislodge the obstruction and restore normal breathing.
Unresponsiveness
Unresponsiveness is a state where a person does not respond to verbal or physical stimuli, indicating a potentially serious medical condition that may require immediate assessment and intervention, including checking for breathing and circulation. Determining the cause of unresponsiveness is crucial for providing appropriate care.
It’s important to clarify that some of the steps you mentioned are not accurate or complete within the context of BLS:
- “Putting a person who is having trouble to sleep”: This is not a BLS procedure. BLS focuses on life-threatening emergencies. If someone is having trouble sleeping, it’s a different medical issue.
- BLS is about keeping someone alive until professional help arrives, not “helping someone to sleep.”

Latest Blog
About the Founders: Our Commitment to Empowering Life-Savers
IMEDICA BLS Canada was founded by a team of dedicated
AED Training: How Imedica Empowers You to Save Lives with Automated External Defibrillators
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a life-threatening emergency that can